What Is The Normal Size Of A Prostate
Anatomy of the prostate
The prostate is a pocket-size gland in the male reproductive system. It is situated in front of the rectum, beneath the bladder, and surrounds the urethra, which is the tube through which urine flows out of the body. The main role of the anecdote-sized prostate is to secrete role of the seminal fluid that combines with sperm to form semen.
What is the normal prostate weight ?
A salubrious adult prostate weighs effectually 20 to 25 grams and is approximately iv cm wide, 3 cm high and 2 cm thick.
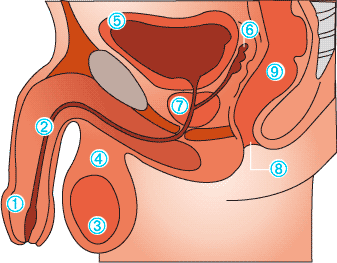
- Penis
- Urethra
- Testis
- Scrotum
- Bladder
- Seminal vesicle
- Prostate gland
- Anus
- Rectum
Size of the prostate
Prostate size remains the same until half of his life (around xl years). Organ's size can only be described by words similar "small", "medium" or "big". However, urologists use volume rather than weight to characterize it. Ultrasound are used to measure this data. Shaped every bit a anecdote, its mutual size is 3 cm high and iv cm broad. Its mutual volume is twenty cm3 for around twenty grams. These data may change from one person to another.
What is the normal prostate size ?
A small prostate has a volume of 30 ml to forty ml and a weight of 20 k to 70 g. A medium prostate has a volume of twoscore ml to 80 ml and a weight of 20 g to 125g . A large prostate has a volume of 40ml to 100 ml and a weight of xl g to 125 1000.
Around age 40, prostate gland begins to grow. With a benign prostatic hyperplasia (a balmy disease), gland's size tin can increase past 4 to 5 times compared to its initial size.
Sources:
Détection précoce du cancer de la prostate, Actualisation du référentiel de pratiques de l'examen périodique de santé (EPS), document PDF , HAS, mai 2013
Diseases of the prostate
Inside the evolution, some disorders can affect the prostate: prostatitis is a prostate infection, prostate adenoma, also called Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH); is a prostate inflammation (abnormal magnification) and prostate cancer (reproduction of abnormal and cancerous cells).
Prostatitis
The term prostatitis – or prostate infection – refers to a swelling of the prostate that commonly occurs to men between 30 and 50 years old. As prostate is linked with urinary and genital tracts, a bacterial contamination of the urethra but also an infection of the entire urinary tract (bladder, urethra, kidneys) may cause prostatitis. In 2005, a study evaluated incidence of prostatitis at one.26 cases per yard men / yr. Most common symptoms are fever, urinary symptoms (frequent urge to urinate, burning sensation, intermittent urination, etc.), lower abdominal hurting, muscle pain or a painful prostate during digital rectal exam. Prostatitis is treated with antibiotics.
Adenoma
Prostate adenoma or benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH) is an abnormal increase of the volume of the prostate. It is beneficial and is often diagnosed when it causes urinary symptoms such as frequent urination, urinary leakage or sexual dysfunction. Adenoma is an enlargement of the prostate that will compress the urethra and cause symptoms. Half of the prostatitis screened will result in a medical treatment for Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy (BPH). On average, 1 in ten men will require surgical handling of their BPH. Disease'south incidence increases with historic period: BPH occurs in more than eighty% of men over 80 years. But changes caused by the phenomenon volition not exist a problem for all men. In absence of complications (retention, infection, renal failure …), medical treatment is the first approach. In second intention, a surgery will restore a correct urination.
Prostate cancer
The human body is fabricated up of cells that carve up and reproduce throughout life. Sometimes the newly created cells are defective and will every bit well multiply, creating more and more abnormal and cancerous cells, and then called cancer. Majority of prostate cancers are adenocarcinomas; they develop from the prostate coating cells.
Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men with more than 1 1000000 new cases diagnosed each yr worldwide (according to the World Cancer Study 2014*: 1 111 689 cases identified in 2012). Notwithstanding, since prostate cancer is a slowly progressive affliction affecting older men, mortality from the disease is moderate (6.6%, or 307,471 deaths in 2012 according to the same report *).
*: ©International Agency for Research on Cancer, 2014 – World Cancer Written report
The risk for developing prostate cancer increases with age: after 45 years in case of family history and from fifty years for anyone else. It'south around lxx years former that the number of cases is the highest. All prostate cancers don't accept the same degree of severity: 80% are discovered at an early, localized phase. The affliction progression is usually slow. Prostate cancer is generally not associated with whatsoever specific symptom: information technology tin be detected during a recommended screening or during a prostate adenoma follow-up.
Prostate cancer screening includes several examinations such as PSA blood test, digital rectal examination, prostate biospies. The diagnosis must be refined by performing a series of imaging examinations for the staging assessment. The purpose of the staging assessment is to accurately determine whether the cancer is localized (i.e. wholly contained within the prostate gland) or has spread. In one case the cancer diagnosed, the urologist will discuss the treatment strategy with the patient.
Prostate cancer hazard factors
- Age
- Hereditary factors
- Ethnic origin
- Fatty nutrition
- Other factors: sedentary lifestyle, obesity, etc.
What Is The Normal Size Of A Prostate,
Source: https://www.hifu-prostate.com/the-prostate2/#:~:text=A%20healthy%20adult%20prostate%20weighs,high%20and%202%20cm%20thick.
Posted by: kennedysence1957.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Is The Normal Size Of A Prostate"
Post a Comment